A Saliency SIFT Feature-Based Method for Image Recommendation
08 Jul 2015Abtract
Current image search and image recommendation show their boundedness in accuracy, because these methods tend to neglect images’ content while focus on textual information searching in the Internet. In order to fully employ images’ information, such as color, style, texture to perform recommendation which is more similar to human’s recognition, a saliency-based SIFT feature extracted method is proposed to acquire detailed information of images. What’s more, a bag-of-words model is applied to better represent images. Finally based on the feature extracted, our recommendation method takes advantage of SVM to depict images’ possibility to certain image category to calculateimage’s distance to users, which approximates human’s view in comparing images. What’s more, a method to extend imagecategories to achieve accurate classification is put forward.
Algorithm Overview
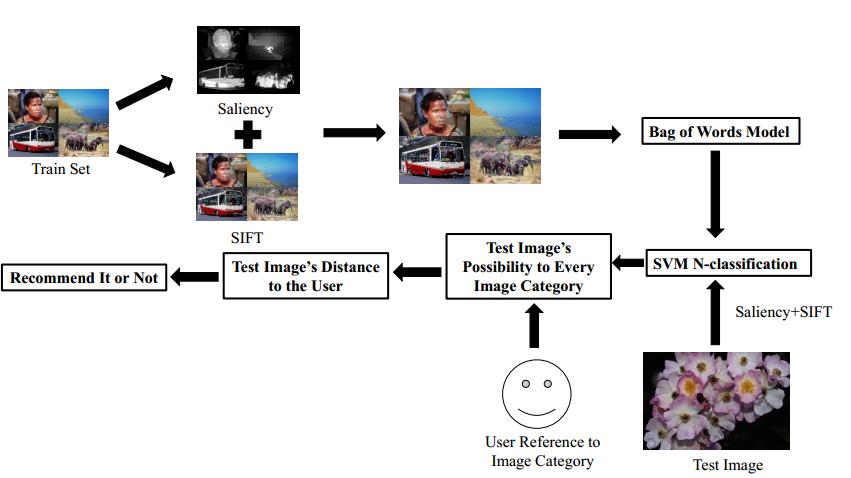
Saliency
In our paper, we used the method in [1] to achieve saliency detection with a robust result. Firstly, a new background measure from a conceptual perspective is derived and then an effective computation method is described. Secondly, the method further discusses the unique benefits originating from its intuitive geometrical interpretation. Finally, the method proposes a principled framework that intuitively integrates low level cues and directly aims for the goal to combine multiple saliency cues or measures.
SIFT bag-of-words
SIFT feature
Scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) algorithm transforms an image into a large collection of feature vectors, each of which is invariant to image translation, scaling, and rotation,partially invariant to illumination changes and robust to localgeometric distortion.
Bag-of-words Model
The bag-of-words(BOW) model originates from natural language processing and information retrieval, commonly used in methods of document classification, where the (frequency of) occurrence of each word is used as a feature for training a classifier.
In our method, SIFT features will be firstly detected. Every image is described as a M * 128 matrix (M represents the number of the SIFT detected). However, different numbers of SIFT features are extracted in one image, which cause difficulty in processing. To solve the problem of dimensional unequality, all image’s SIFT features are collected and clustered into K clusters (K is the user definite) to form the codebook which is a K*128 matrix, and every row is the centroid of a cluster). Codebook can be viewed as a standard of features where every image’s SIFT features find its nearest centroid in the codebook.
After all the features of a image are mapped to the codebook, a K dimension histogram is used to record the frequency of every matched codeword, representing the image in the BOW model. Algorithm.1 describes the process.
SVM Based Similarity
Images contains various objects and partitions. Even art master can not definitely state two images are similar, while people tend to attribute images to certain categories or how much it belongs to certain categories. Therefore, assumption can be made that images are similar because that they belongs to the same category or they partly belongs to some same categories. Therefore, we propose a similarity calculation method to measure the distance between two images by multiplying how much image i belongs to category c and how much image j belongs to category c for all the categories.
Recommendation System
To define our recommendation algorithm, first to define the records used in our methods. As a user browses images (In our experiment, what the users browse come from training set), the system will record the image index that the user get interested in. For a given user, record will be {imagei; imagej; imagek; …}. For a given record, the algorithm first specifies the user’s reference, or how much the user favors certain category.
For instance, the algorithm will calculate the categories distribution in the records, category one for 40%, category two for 30% etc. For every image in the recommended set (In our experiment, the test set), the algorithm will calculate their distance from the user by summing up image’s possibility to certain category multiply how much the user are in favor of this category.
Experiment
 The figure above demonstrate 5 set of experiment results. Every set contain 5 input images and 3 output(recommended images). The left column images are users’ interested images while the right ones are recommended. The display order of recommended images is according to the how strongly the system want to recommend the image to the user. The left ones are the most recommended images.
The figure above demonstrate 5 set of experiment results. Every set contain 5 input images and 3 output(recommended images). The left column images are users’ interested images while the right ones are recommended. The display order of recommended images is according to the how strongly the system want to recommend the image to the user. The left ones are the most recommended images.
Reference
[1] W. Zhu, S. Liang, Y. Wei, and J. Sun, “Saliency optimization from robust background detection,” in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2014 IEEE Conference on, 2014, pp. 2814 – 2821.